Integrins
Cell ≫ 세포골격 ≫ ECM
세포 - Integrins
세포골격, ECM
- 증점(단순)다당류 , 복합다당류
- 세포는 Fiber 덩어리다 , 세포는 콜라겐 덩어리다
- 콜라겐 Collagen , 콜라겐 조성 및 합성과정
- 엘라스틴 elastin, Proteoglycan
- Fibronectin, Laminins
- Integrins, Cadherins
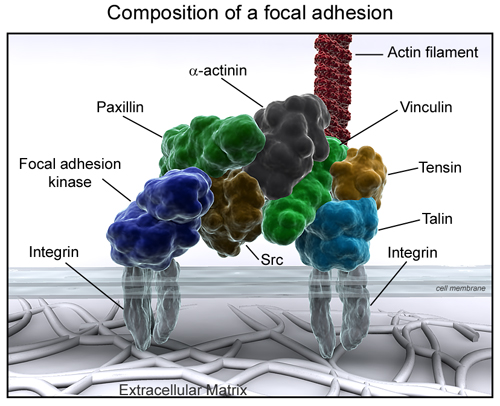
1. integral, transmembrane proteins of PM
2. link the ECM with cytoskeleton thru PM protein
a. external domain of protein has binding site for ECM
-binding site for fibronectin, -binding site for laminin
b. internal domain of protein has binding site for cytoskeleton
-binding site for talin
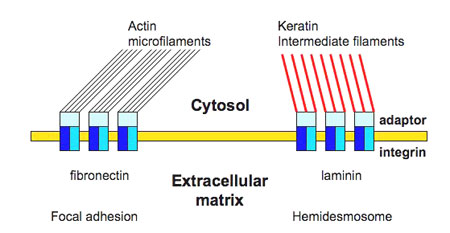
-green = microfilament
-purple = antibody for integrin
-vinculin binds talin
-vinculin also binds microfilaments
-so, ECM can be connected to microfilaments!
3. structure of Integrins
a. two transmembrane polypeptides
b. noncovalent association
c. complex produces the binding sites
-isolated monomers are inactive
d. multiple types of alpha and beta subunits
-get many different heterodimers
-different heterodimers have different functions
-eg: heterodimers with beta-1 subunit found all cells
-used to connect PM to ECM
-eg: heterodimers with beta-2 subunit found
only on white blood cells
-used in cell-cell recognition
|
|
Network ≫ 두뇌, 마음, 욕구
뇌의 작동원리, 지도원리
감각 기관
보상시스템
- 학습 파페츠
- 목적 동기 부여 회로
식욕 mechanism
- Food Pleasure
file.txt
file.txt
|