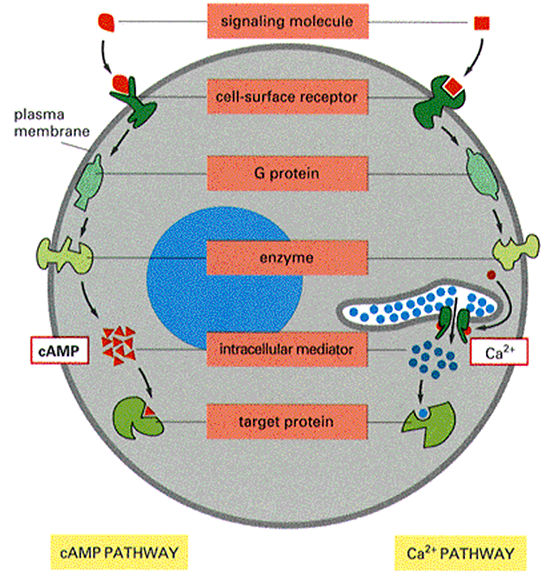
조절물질 ≫ 신경전달, 호르몬 ≫ 2차전령
Cyclic AMP(cAMP) path
신경전달물질 : 2차 전령
- NO, CO
- cAMP, 칼슘
G단백 System : GPCR
- cAMP path, IP path, 탈감작
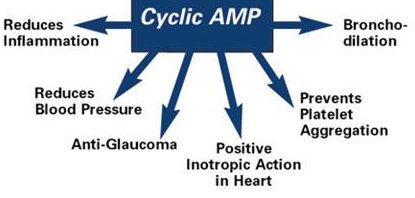
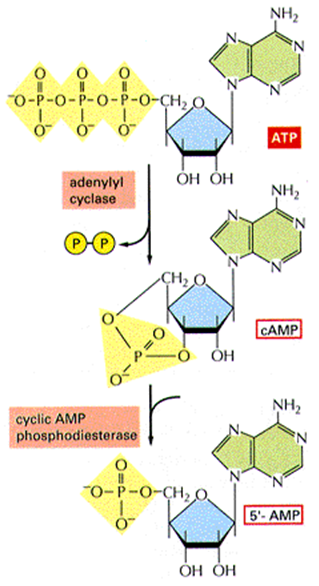
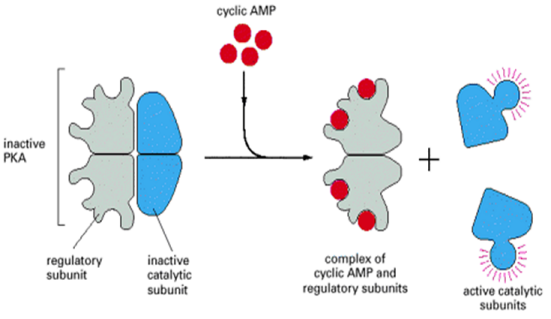
cAMP

- from adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
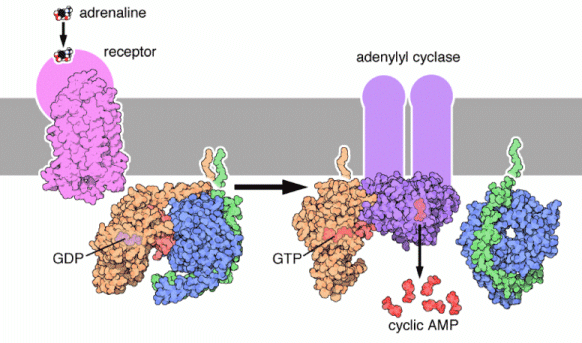
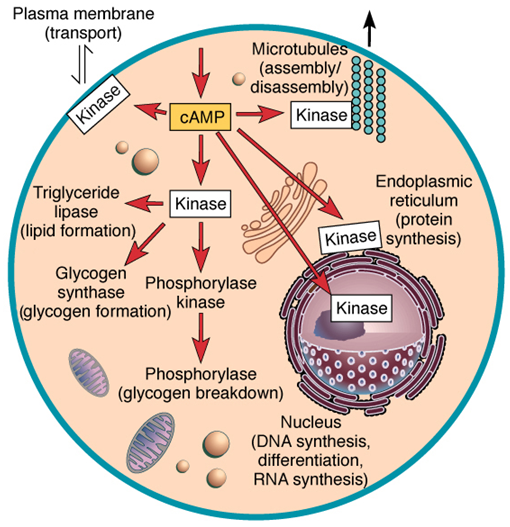
The cAMP Dependent Pathway is used as a signal transduction pathway for many hormones including:
ADH - Promotes water retention by the kidneys (V2 Cells of Posterior Pituitary)
GHRH - Stimulates the synthesis and release of GH (Somatotroph Cells of Anterior Pituitary)
GHIH - Inhibits the synthesis and release of GH (Somatotroph Cells of Anterior Pituitary)
CRH - Stimulates the synthesis and release of ACTH (Anterior Pituitary)
ACTH - Stimulates the synthesis and release of Cortisol (zona fasiculata of adrenal cortex in kidneys)
TSH - Stimulates the synthesis and release of a majority of T4 (Thyroid Gland)
LH - Stimulates follicular maturation and ovulation in women; Stimulates testosterone production and spermatogenesis in men
FSH - Stimulates follicular development in women; Stimulates spermatogenesis in men
PTH - Increases blood calcium levels (PTH1 Receptor: Kidneys and Bone; PTH2 Receptor: Central Nervous system, Bones, Kidneys, Brain)
Calcitonin - Decreases blood calcium levels (Calcitonin Receptor: Intestines, Bones, Kidneys, Brain)
Glucagon - Stimulates glycogen breakdown (liver)
hCG - Promotes cellular differentiation; Potentially involved in apoptosis
Gαi inhibits the production of cAMP from ATP.
Gαq/11 stimulates membrane-bound phospholipase C beta, which then cleaves PIP2 (a minor membrane phosphoinositol) into two second messengers, IP3 and diacylglycerol (DAG).