원료 ≫ 비타민 ≫ 비타민 C
비타민C : 합성
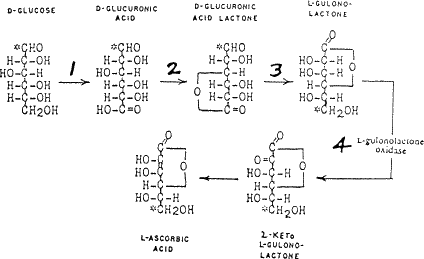
식물의 Vitamin C 천연합성

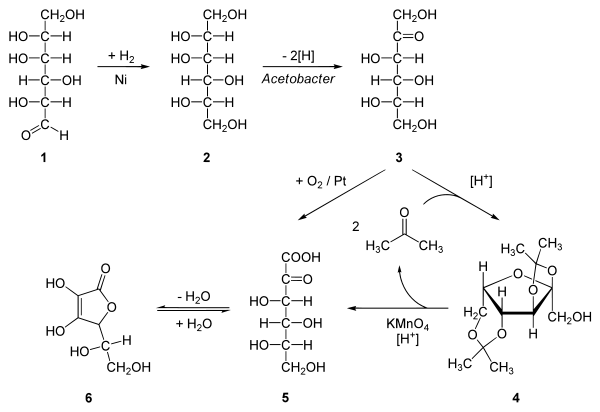
화학적(산업적) 합성
hydrogenation of D-glucose to D-sorbitol, an organic reaction with nickel as a catalyst under high temperature and high pressure. Microbial oxidation or fermentation of sorbital to L-sorbose with acetobacter [1] with pH 4-6 and 30 °C. protection of the 4 hydroxyl groups in sorbose by formation of the acetal with acetone and an acid to Diacetone-L-sorbose (2,3:4,6−Diisopropyliden−α−L−sorbose) Organic oxidation with potassium permanganate followed by heating with water gives the 2-Keto-L-gulonic acid The final step is a ring-closing step or gamma lactonization with removal of water .[2] Intermediate 5 can also be prepared directly from 3 with oxygen and platinum