| Hint | Food | 맛과향 | Diet | Health | 불량지식 | 자연과학 | My Book | 유튜브 | Frims | 원 료 | 제 품 | Update | Site |
|
식품 ≫ 지방 General characters of lipids are Lipids are relatively insoluble in water. They are soluble in non-polar solvents, like ether, chloroform, methanol. Lipids have high energy content and are metabolized to release calories. Lipids also act as electrical insulators, they insulate nerve axons. Fats contain saturated fatty acids, they are solid at room temperatures. Example, animal fats. Plant fats are unsaturated and are liquid at room temperatures. Pure fats are colorless, they have extremely bland taste. The fats are sparingly soluble in water and hence are described are hydrophobic substances. They are freely soluble in organic solvents like ether, acetone and benzene. The melting point of fats depends on the length of the chain of the constituent fatty acid and the degree of unsaturation. Geometric isomerism, the presence of double bond in the unsaturated fatty acid of the lipid molecule produces geometric or cis-trans isomerism. Fats have insulating capacity, they are bad conductors of heat. Emulsification is the process by which a lipid mass is converted to a number of small lipid droplets. The process of emulsification happens before the fats can be absorbed by the intestinal walls. The fats are hydrolyzed by the enzyme lipases to yield fatty acids and glycerol. The hydrolysis of fats by alkali is called saponification. This reaction results in the formation of glycerol and salts of fatty acids called soaps. Hydrolytic rancidity is caused by the growth of microorganisms which secrete enzymes like lipases. These split fats into glycerol and free fatty acids. 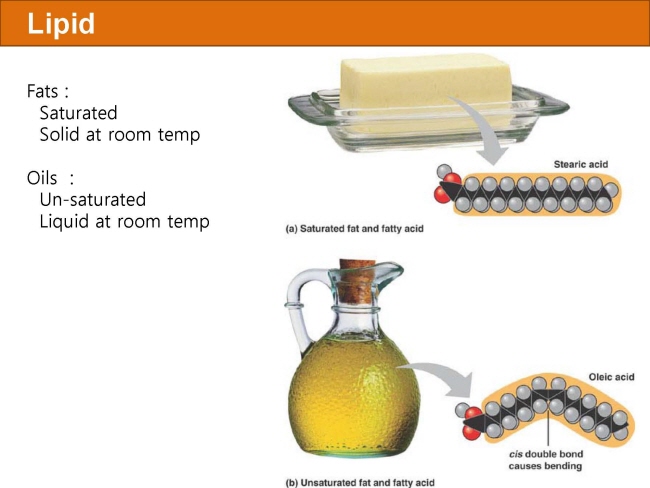 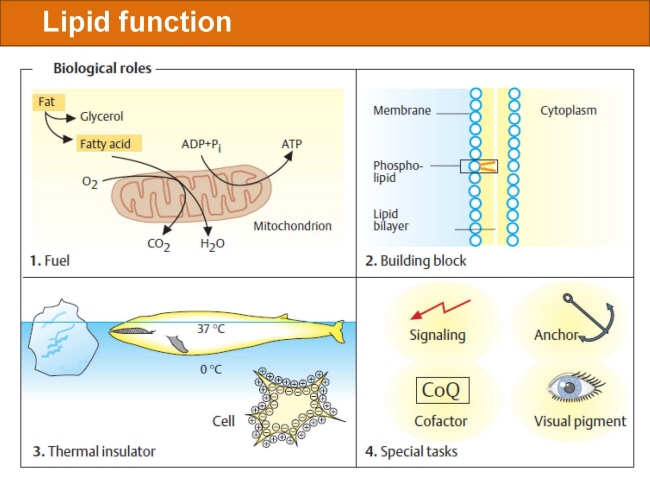 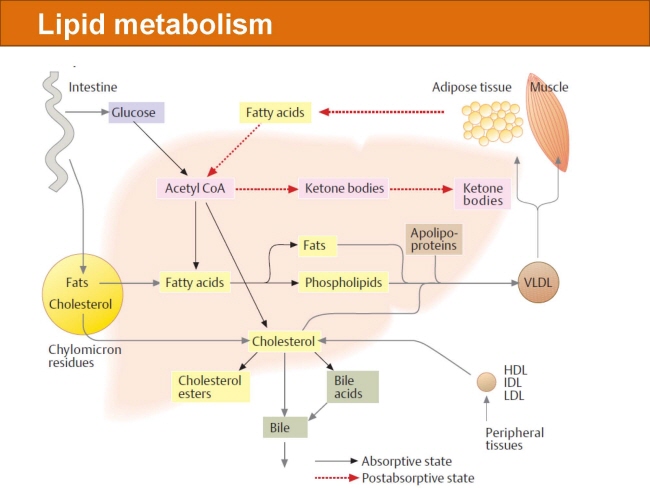 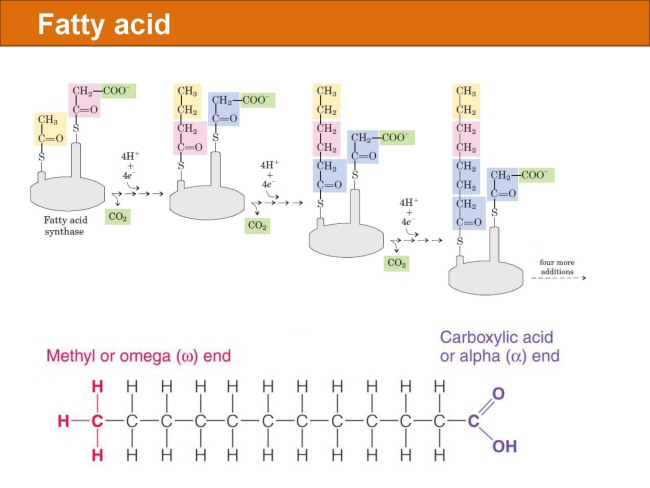 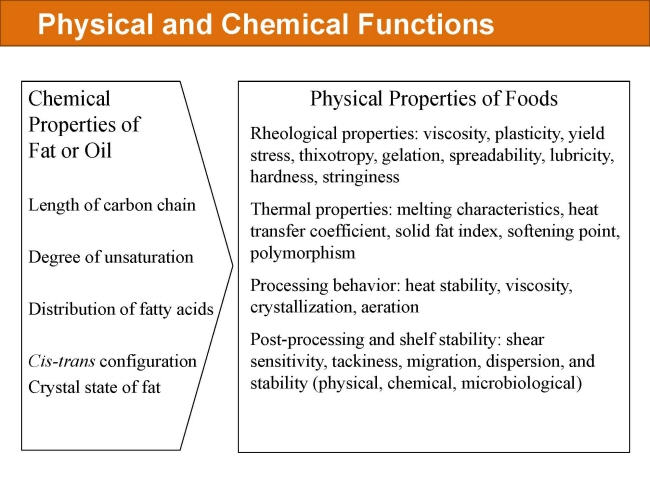  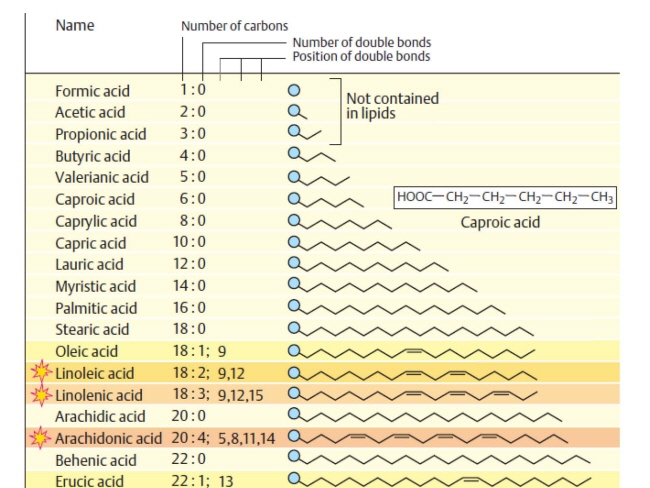 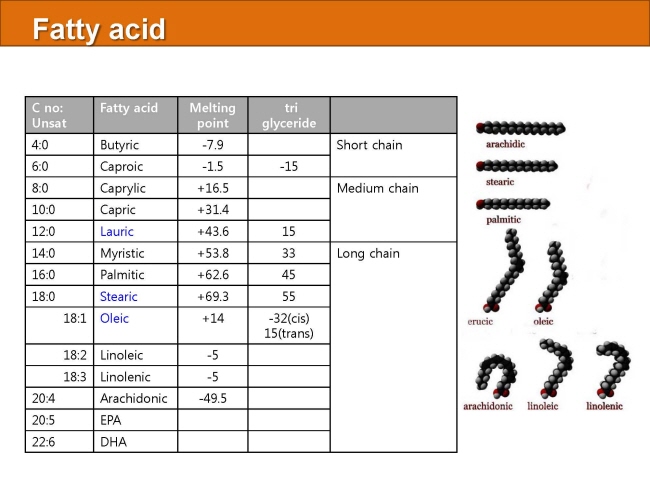 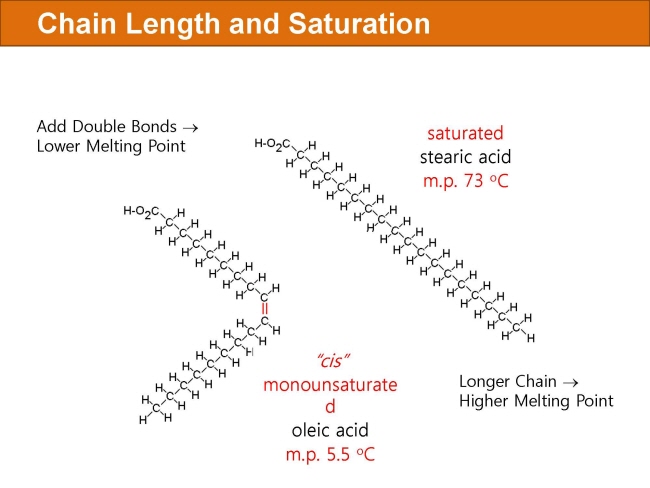 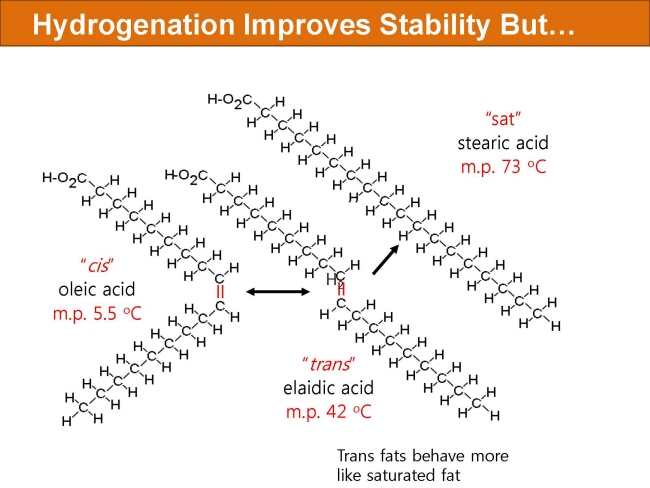 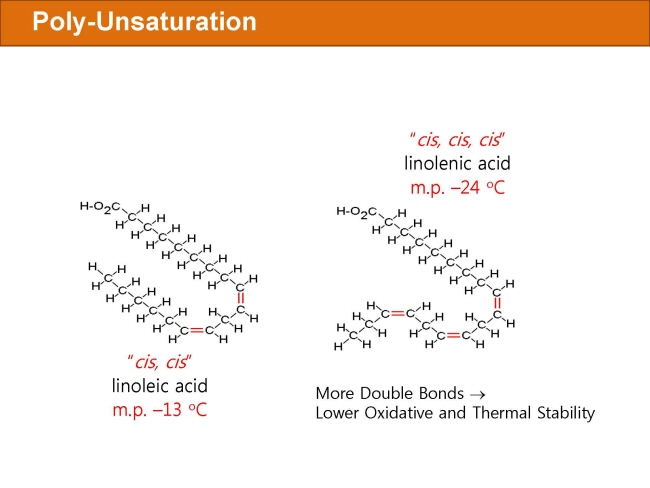 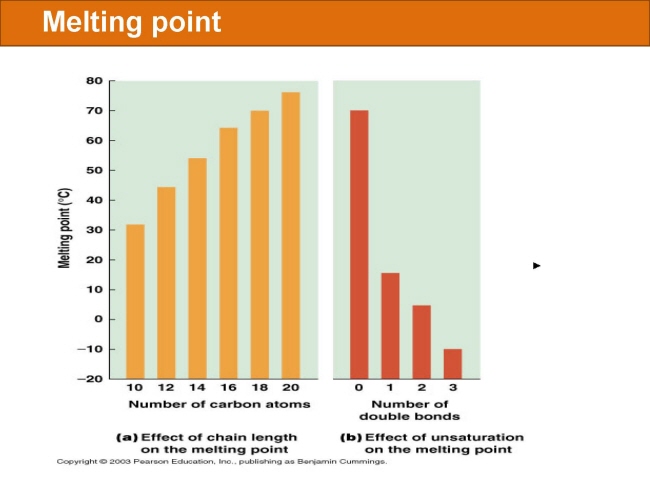 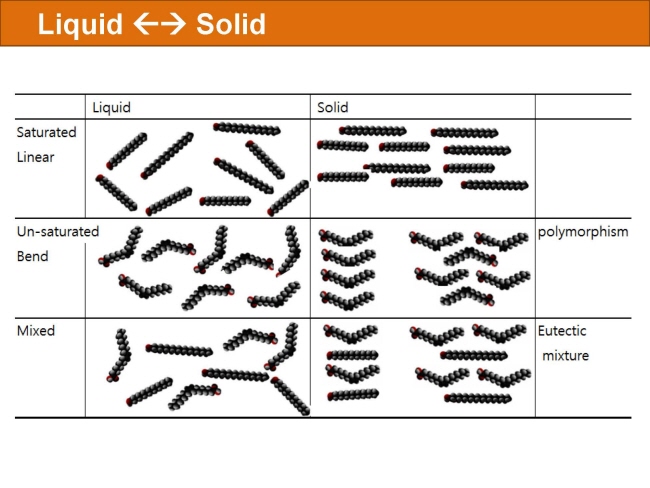 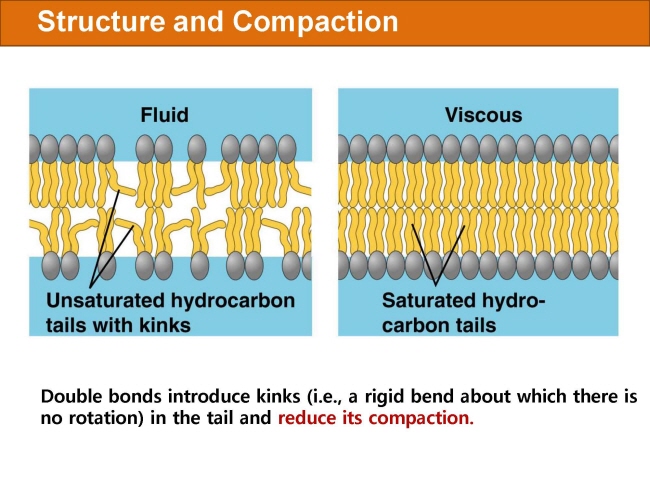 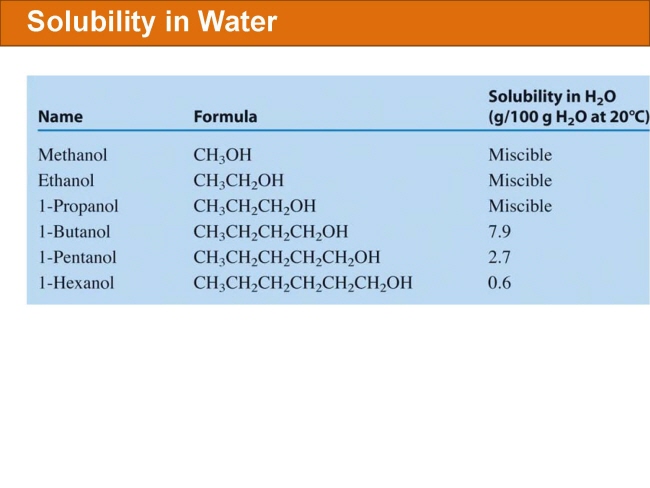 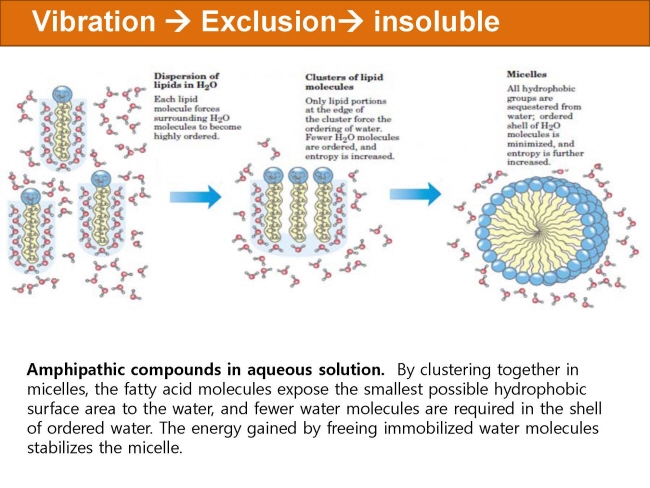 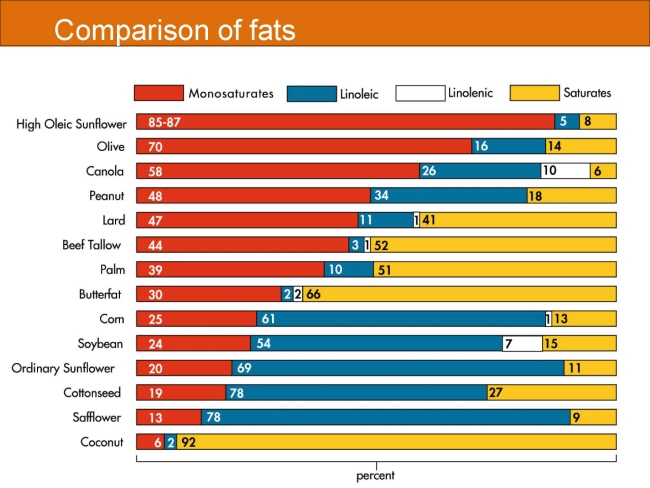 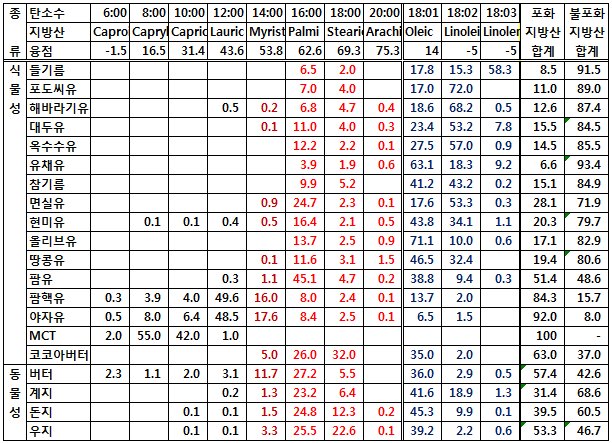  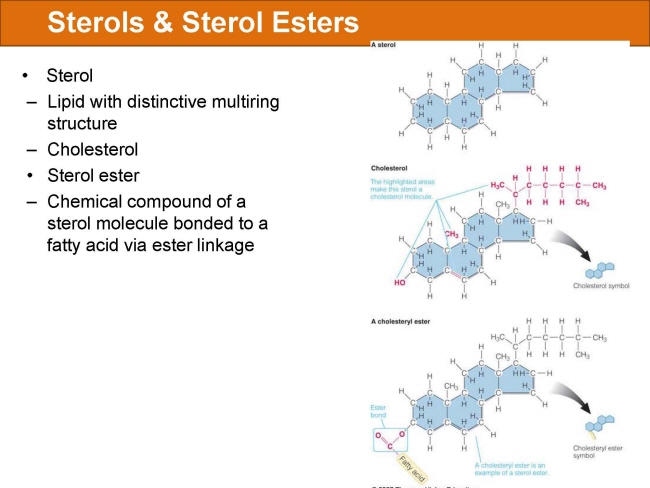  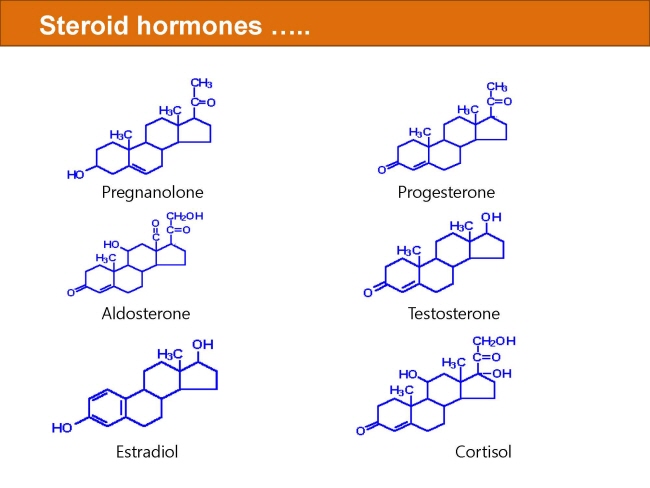 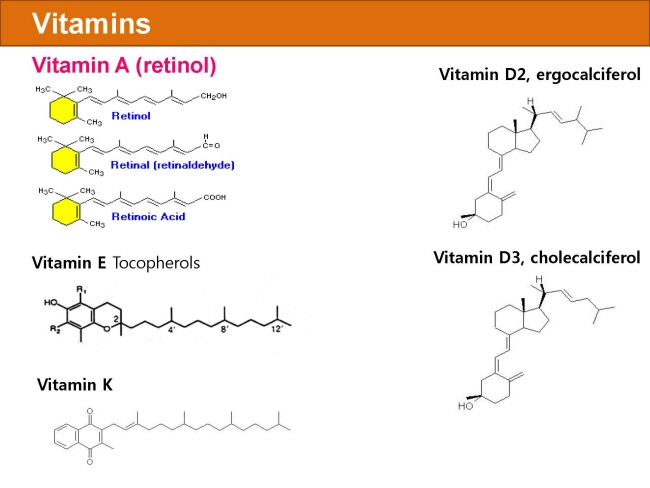 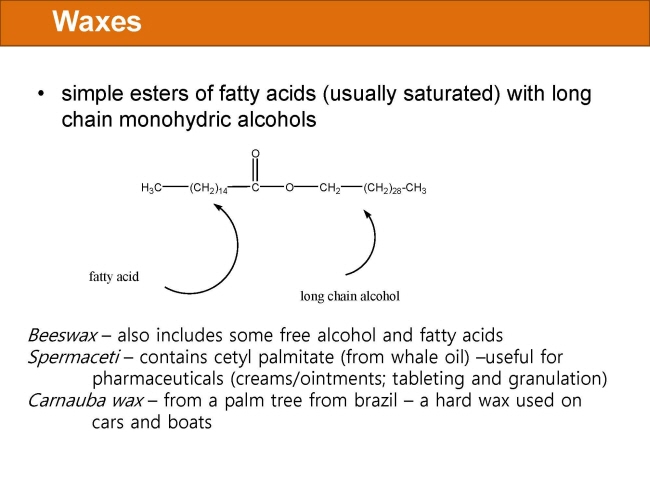 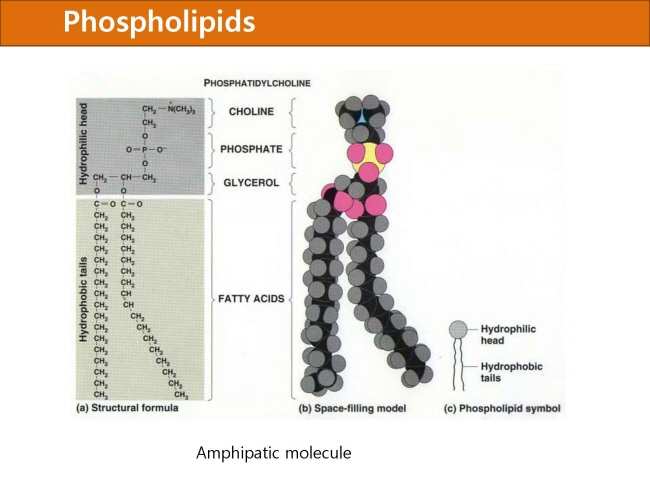  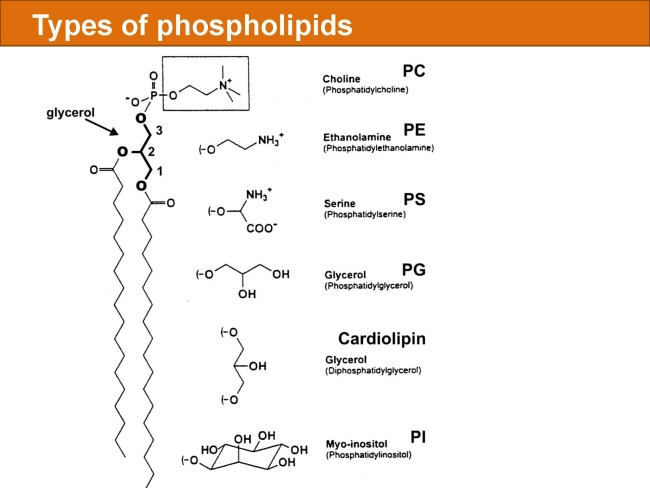 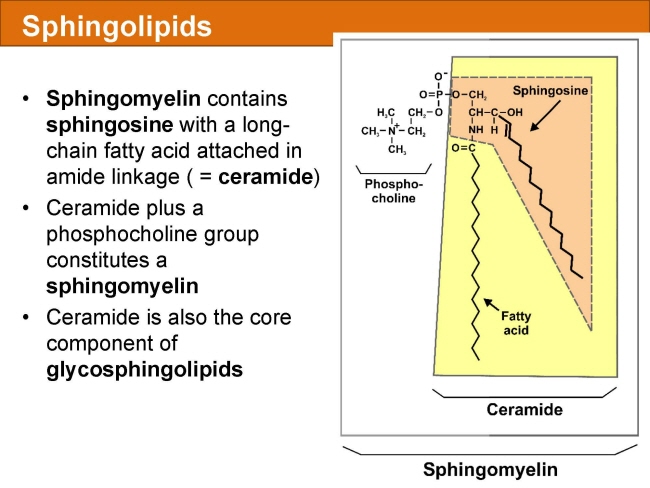 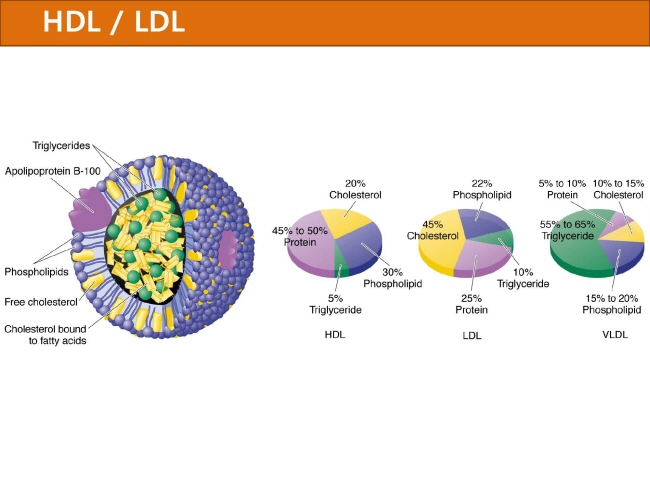 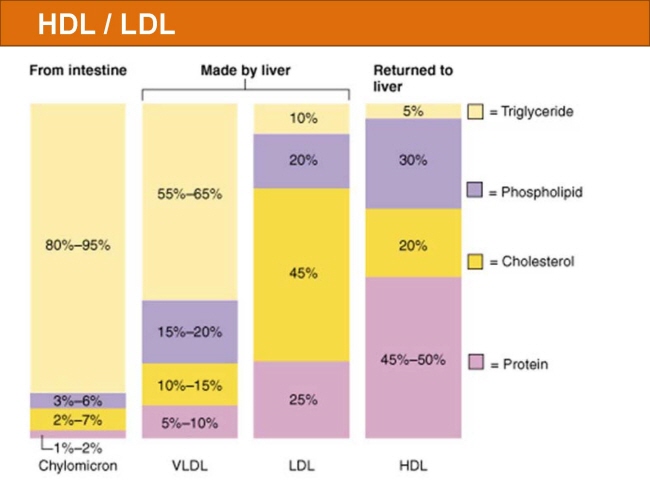 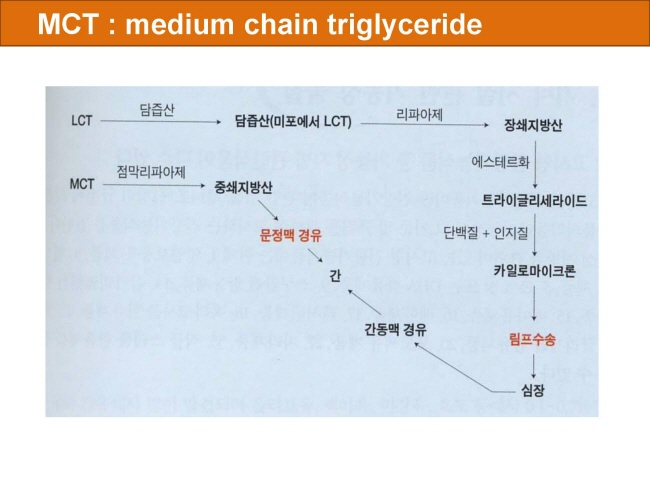 |
||||
|
|
|||